BLENDER PLUGIN PROPERTIES
IMPORTANT! This part of the documentation has not been fully updated for Microsoft Flight Simulator 2024 and is currently a work in progress.
This page outlines the main properties of the Blender add-on for Microsoft Flight Simulator 2024.
Materials
When you select an object in Blender, you can access the material properties from the Object Ribbon on the right, under the Material Properties button.
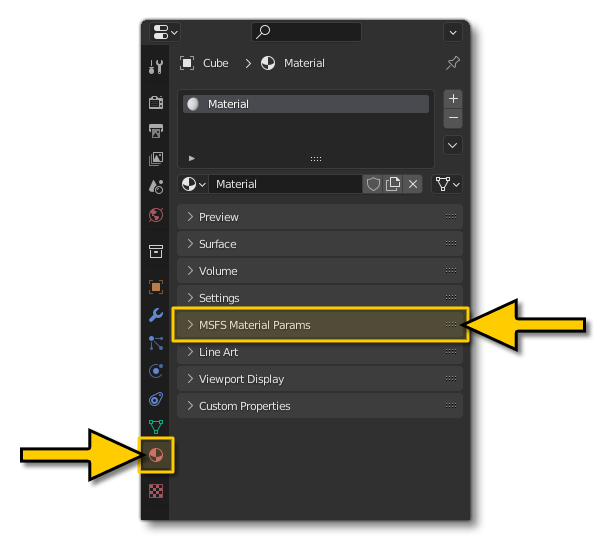
Expanding this section will permit you to choose from the available materials, and then configure the available options based on the material type. You can find all the information these materials from the following page:
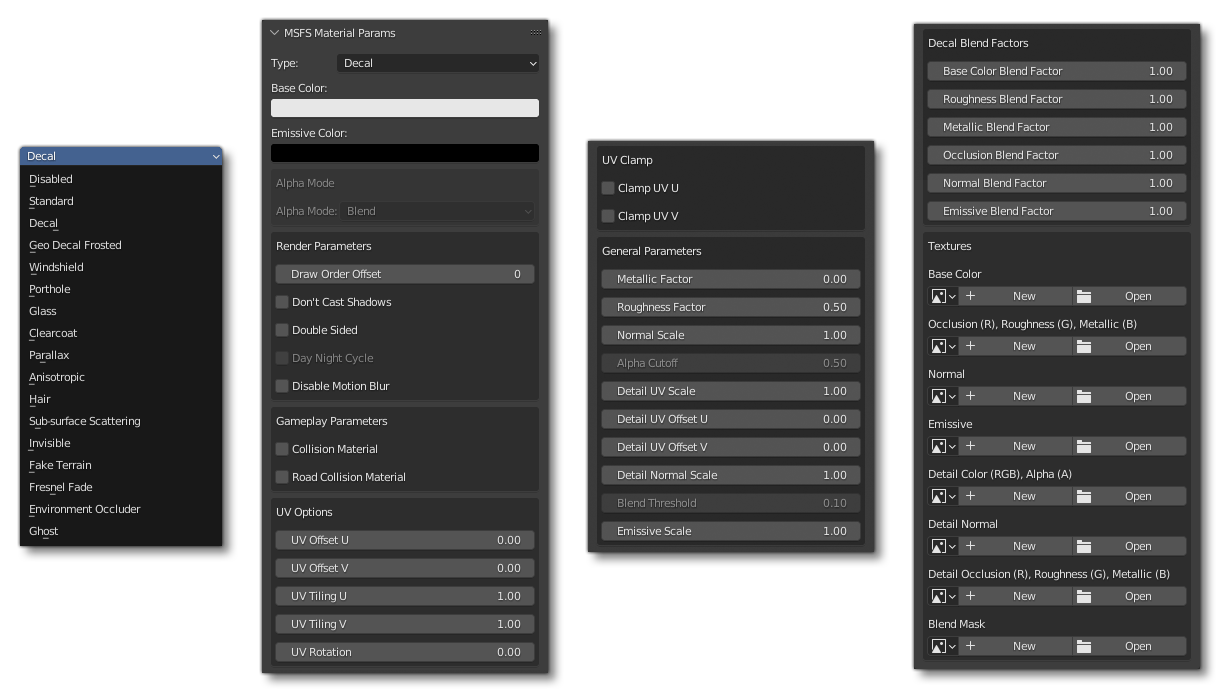
When you want to export a model specifically for Microsoft Flight Simulator 2024, you need to ensure that it is set to a dedicated Flight Simulator material, for example:

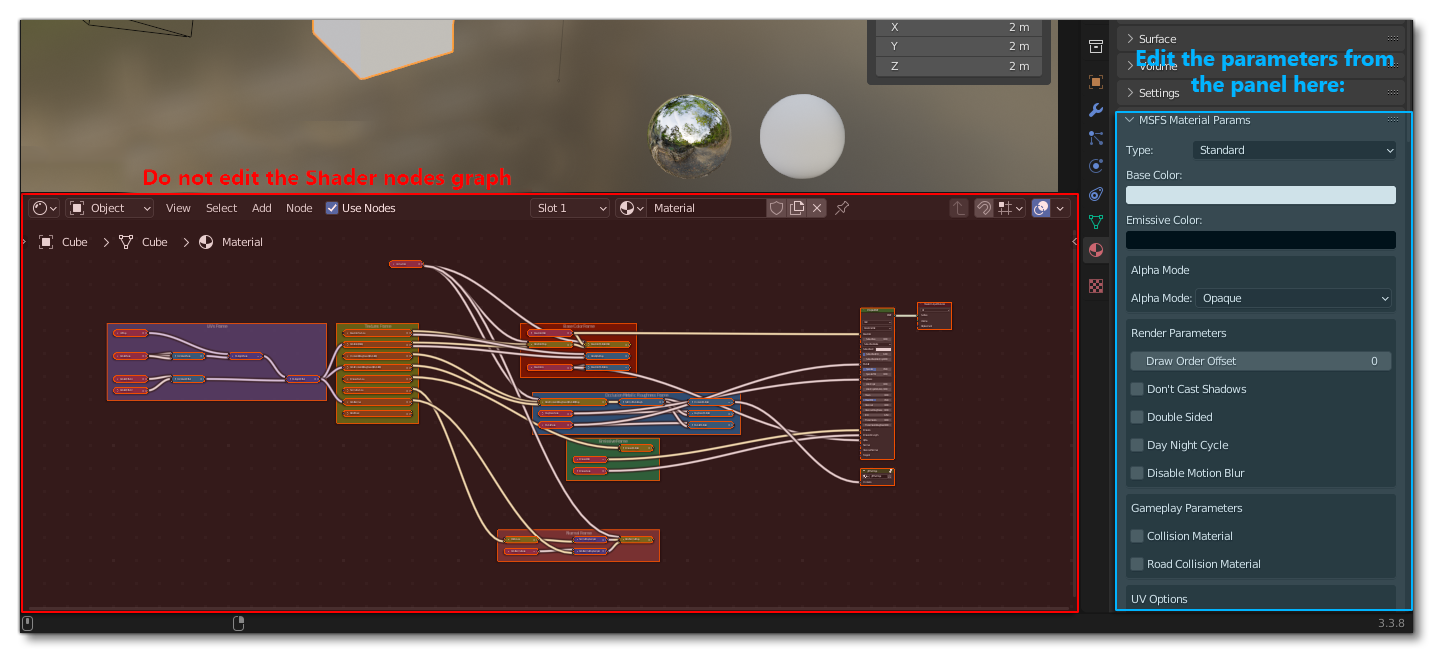
When you set a Flight Simulator material, you have to edit the material properties from the MSFS material parameters only:

Do not edit the shader nodes graph directly, as it will break the model export.
Light Properties
When you are ready to start adding lights to your model in Blender, you'll see that there are number of parameters in the MSFS Properties that can be set:

To find out more about these parameters, please see the following page:
Objects Parameters
When you select an object, you can find a number of additional options that have been added by the MSFS 2024 Blender plugin:

-
Override Unique ID
When this is selected, an input box will be shown where you can give an ID to override the object-specific unique ID.
-
Transform Properties
This section lets you set whether to reset the translation / rotation / scale of the object when it is exported. Note that these options will be overridden by the Reset Origins options in the Export Settings.
-
Mesh Parameters
This section has the following option:- IsSoftbodyMesh - When this is checked, the object mesh will be considered a "soft body mesh" linked to a physics mesh for the simulation of a hot air balloon canopy in the simulation. It is not used for anything other than the creation of hot air balloons.
Image Properties
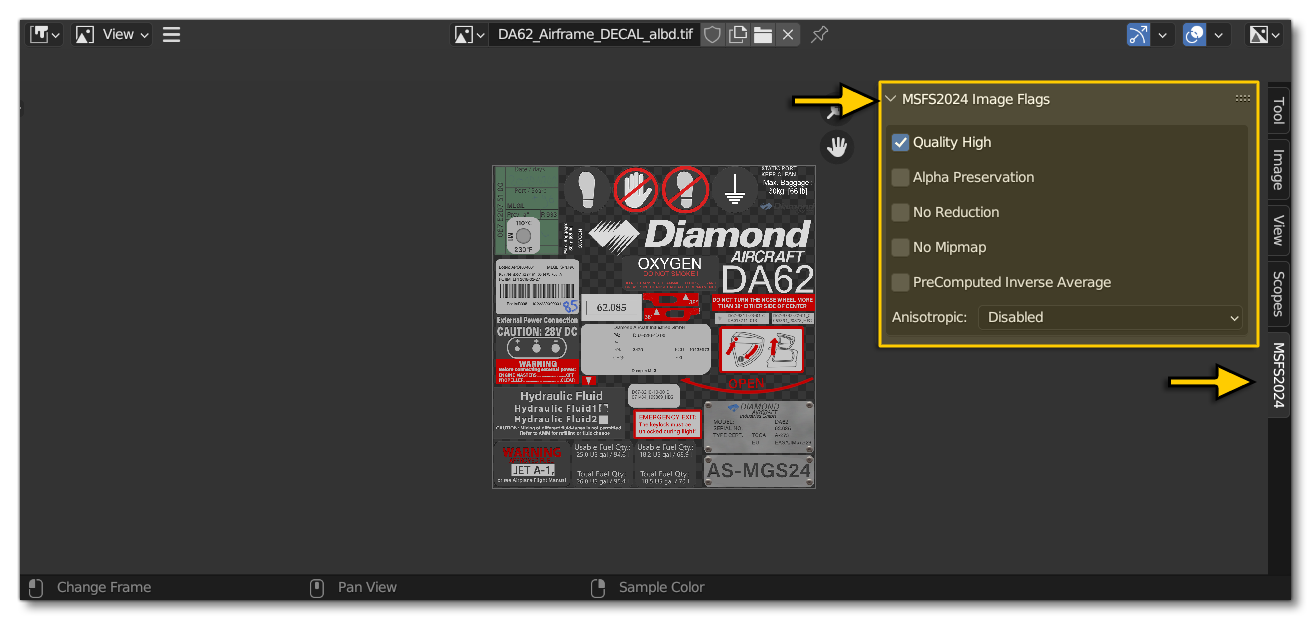
In Microsoft Flight Simulator 2024, for optimisation and flexibility within the simulation, you now have to provide a texture XML file for each texture of the model. Given that a single model can have numerous textures (and therefore require an equal number of XML files), these files are exported by default along with the glTf by ticking the Generate TextureLib option in the Settings Panel export preset. There you can also set up some flags for your textures in the MSFS2024 Images Flags panel using the Image Editor in Blender:
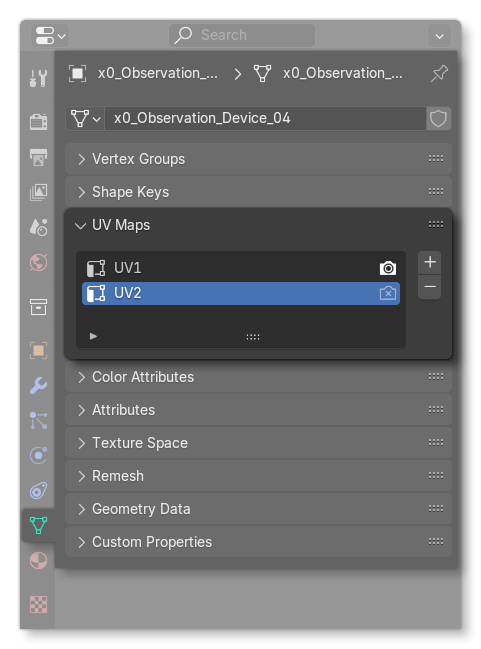
UV2 Channels
If a material requires a secondary UV map, this must be named UV2 and only UV2, for the following two reasons:
- To correctly preview the UV2 map in the Blender viewport.
- To ensure proper behavior when using the "Merged nodes" export setting - objects will only merge correctly if the second UV map is named UV2.
You may also rename the primary UV map to UV1, but this is optional. Blender determines the active UV map based on user selection, not the name.
Vertex Colour Setup
When using the Blender add-on, a default white vertex color attribute is automatically added to all new objects. This is required for the add-on's shader system to function correctly:

The vertex color attribute follows this specification:
- Name: Color
- Domain: Face Corner
- Data Type: Byte Colour (RGBA, 8-bit float)
This ensures a consistent baseline for shader effects that rely on vertex colors. This is very important because the MSFS 2024 shaders use the active vertex color attribute, and if an object has no vertex color attribute, it will appear black by default (Blender outputs black vertex color when no color attribute is present). It should be noted too that when using the Merged Nodes export option, all object vertex color attributes must follow the same specification (name, domain, and data type) to be merged correctly.
IMPORTANT! Objects with vertex color attributes that differ in name, domain, or type will not be merged together.
Therefor we recommend the following when dealing with vertex colours:
- Leave the default Color attribute untouched.
- If you add additional vertex color attributes, ensure the correct one is active before export.
- Verify that the active attribute's name, domain, and data type match those of the default Color attribute listed above.
Related Topics