CHARTER SERVICE
In Microsoft Flight Simulator 2024 career mode, you have the possibility of flying charter flights. These flights require you to fly a VIP to famous tourist destinations around the world, or - with the help of a copilot and cabin crew - fly them to exclusive events synchronized with real events around the world. If you wish your aircraft to be used on these activities you will need a preset that has been appropriately set up as part of the Modular SimObject, as explained below.

For more information on the various other career activities and how to prepare your aircraft, please see here:
Charter Activity Constraints
When setting up your aircraft for charter flights you will need to ensure that it fulfills the requirements for such an activity. To start with these activities will require a plane and currently do not support helicopters. The plane will need to meet the following specifications based on the type of charter activity to be performed:
-
Private Charter (Solo)
This kind of flight requires a small plane (like the DA62, for example) which has space for at least one passenger. The following constraints apply:- The plane will need to have the
navigation_graph_pilot.cfg(as explained here). - The aircraft will need to have the
ApronWithoutCovers.fltfile (as explained below). - The
targeted_specializationsmust include thePRC-PSOdressing code. - The
object_classmust be "Airplane". - The
operating_statusmust be either "in_service" or "experimental". - The plane cannot be flagged as military.
- The plane cannot have a copilot.
- The aircraft complexity must also be simple, as explained here: Note On Aircraft Complexity.
- The plane
ui_max_rangemust be greater than 1. - The plane can only sit up to 16 passengers (ie: up to 16
SITnodes, see here for information). - The plane can have wheels or big wheels, for landing gear.
- The plane cannot have skis or floats for landing gear.
Following the constraints given here will give the aircraft the
COF_Cabintype. See here for more information: Note On Cabin Codes - The plane will need to have the
-
VIP Charter (Copilot)
This kind of flight requires a small-to-medium plane (like the PC12 NGX, for example) which has space for at least one passenger. The following constraints apply:- The plane will need to have the
navigation_graph_pilot.cfg(as explained here). - The aircraft will need to have the
ApronWithoutCovers.fltfile (as explained below). - The
targeted_specializationsmust include thePRC-PLCdressing code. - The
object_classmust be "Airplane". - The
operating_statusmust be either "in_service" or "experimental". - The plane cannot be flagged as military.
- The plane must be flagged as premium.
- The plane must have a copilot, and the
sharedSeatparameter for the node must be false (as explained here). - The plane
ui_max_rangemust be greater than 1. - The plane takeoff weight must be less than 44092lbs (as defined by the
max_takeoff_weightparameter). - The plane can have wheels or big wheels, for landing gear.
- The plane cannot have skis or floats for landing gear.
Following the constraints given here will give the aircraft the
PRC_Cabintype. See here for more information: Note On Cabin Codes - The plane will need to have the
-
VIP Charter (Airliner + Cabin Crew)
This kind of flight requires a large plane (like the A320 Neo, for example) which has room for both passengers and cabin crew. The following constraints apply:- The plane will need to have the
navigation_graph_pilot.cfg(as explained here). - The aircraft will need to have the
ApronWithBatteriesWithoutCovers.fltfile (as explained below). - The
targeted_specializationsmust include thePRC-PCCdressing code. - The
object_classmust be "Airplane". - The
operating_statusmust be either "in_service" or "experimental". - The plane cannot be flagged as military.
- The plane must be flagged as premium.
- The plane must have a copilot, and the
sharedSeatparameter for the node must be false (as explained here). - The plane
ui_max_rangemust be greater than 1. - The plane takeoff weight must be greater than or equal to 44092lbs (as defined by the
max_takeoff_weightparameter). - The plane can have wheels or big wheels, for landing gear.
- The plane cannot have skis or floats for landing gear.
-
Following the constraints given here will give the aircraft the
PRC_Cabintype. See here for more information: Note On Cabin Codes - The aircraft must have three
[INTERACTIVE POINTS]of the following types setup:- 0 - Main entrance/exit for catering.
- 0 - Main entrance/exit for ramp or jetway.
- 1 - Cargo entrance/exit.
- The
[SERVICES]must haveBAGGAGE_LOADER,CATERING_TRUCK, andBOARDING_RAMPand/orJETWAYset to true (1).
- The plane will need to have the
Mission Flow - Solo Charter
The flow for performing solo charter flights is as follows:
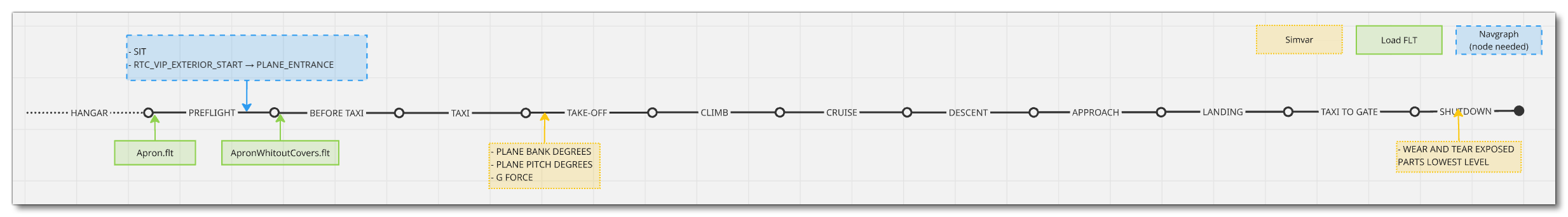
This flow will also require the aircraft to be setup for - and follow - the General Career Mode Requirements.
Mission Flow - VIP Charter
The flow for performing VIP Charter flights is as follows:
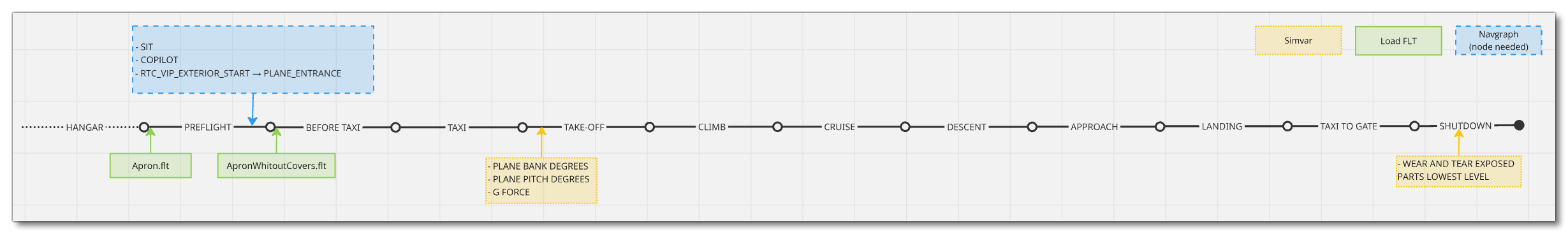
This flow will also require the aircraft to be setup for - and follow - the General Career Mode Requirements.
Mission Flow - VIP Charter Airliner
The flow for performing VIP Charter Airliner flights is as follows:
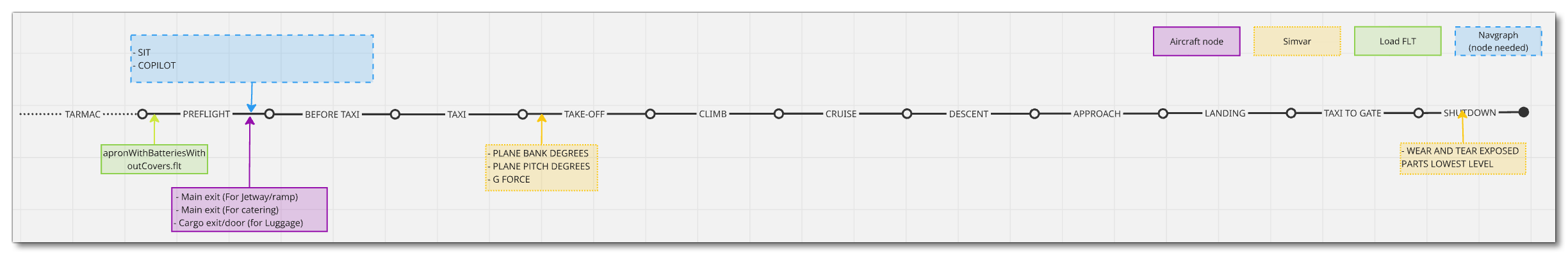
This flow will also require the aircraft to be setup for - and follow - the General Career Mode Requirements.
SimVars
While not directly influencing the mission flow, the following SimVars are important for ensuring a smooth user experience without frustrations. These are what are used in the simulation code to decide whether the user should receive a penalty on their mission score or not, and as such, particular attention should be paid to ensure that these are always returning correct values.
| Penalty | SimVar | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Smoothness Score | PLANE BANK DEGREES |
This is used to check the banking angle of the aircraft while performing the first flight / tour. |
PLANE PITCH DEGREES |
This is used to check the pitch angle of the aircraft while performing the first flight / tour. | |
G FORCE |
This is used to check the G forces applied in the aircraft to passengers while performing maneuvers. | |
| Aircraft Condition | WEAR AND TEAR EXPOSED PARTS LOWEST LEVEL |
This is needed to compute aircraft damage, based on the most damaged part, at the end of the mission. |
Navigation Graph Setup
For charter flights, the navigation_graph_passenger.cfg file is required, which can be added to the base files in the common folder, or into a folder placed in the preset specific to the activity (which will be merged with the base file as part of the Modular SimObject Merging process). Either way, the the navigation_graph_passenger.cfg file must have the following three nodes defined:
-
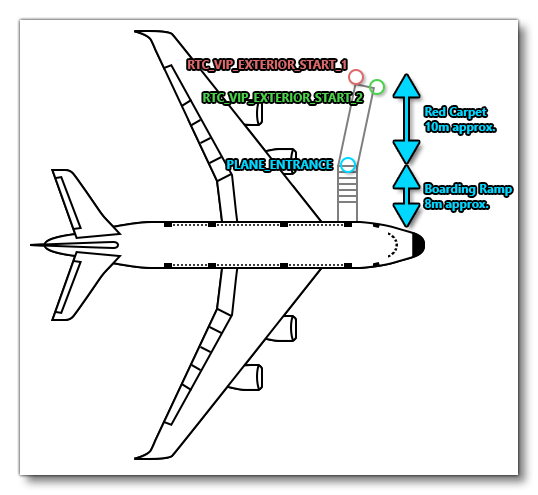
RTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_1
This node is the node where the "VIP" passenger will spawn into the world at the start of the activity. For charter activities there is a short RTC animation that will play of the passenger moving from this point to thePLANE_ENTRANCEnode before entering the aircraft. This node should be on the left side of the aircraft, approximately 8-10m away from the correspondingPLANE_ENTRANCEnode, and be connected to that node with an edge.
-
RTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_2
This node has the exact same conditions for placement as theRTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_1node. It should be placed at the approximate same position too (although a little variation is permitted), since the node will be used to recreate an "american shot" (also called "cowboy shot") cut-scene as part of the initial activity RTC of the VIP moving towards thePLANE_ENTRANCE. This node should be on the left side of the aircraft, approximately 8-10m away from thePLANE_ENTRANCEnode, and be connected to that node with an edge.
-
PLANE_ENTRANCE
This node is only required if you have not set one up already as part of the Passengers navigation graph. It defines the point where the passenger would enter into the plane, and for small and medium aircraft this would be a point right next to the aircraft fuselage, where the door is. For large airline type planes, this point will be approximately 8m from the fuselage door to leave space for the boarding stairs (see the image below). Both theRTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_1andRTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_2nodes should be connected to this node using an edge.
The image below illustrates how these nodes should be setup for an airliner:
Your aircraft navigation_graph_passeneger.cfg file will also need additional nodes for the passenger seats, as many as outlined in the constraints for the aircraft (explained above). These nodes should spawn seat logic objects, and each seat logic object should have the SIT node. You may also need to add a seat object that has the COPILOT node, depending on the mission. You can find more information here:
Here, for example, we have the navigation graph set up with the nodes listed above, as well as additional nodes to spawn the seat logic objects - SEAT_PAX_1, SEAT_PAX_2, etc... - where each one will have the SIT node:
[NODE.1]
name= EXTERIOR_START_1
pos = -5,-3.48502,-1.323018
pbh = 0,0,0
tag = RTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_1
edgeToMainNode = 0
projectOnGround = true
[NODE.2]
name= EXTERIOR_START_2
pos = -5,-3.524884,0.547803
pbh = 0,0,0
tag = RTC_VIP_EXTERIOR_START_2
edgeToMainNode = 0
projectOnGround = true
[NODE.3]
name= ENTRANCE
pos = -34,-3.607832,-1.87888
pbh = 0,0,90
tag = PLANE_ENTRANCE
edgeToMainNode = 0
projectOnGround = true
[NODE.4]
name= ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_1
modelNode = ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_1
interactiveObject = SEAT_PAX_1
massSection = Left_pax
[NODE.5]
name= ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_2
modelNode = ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_2
interactiveObject = SEAT_PAX_2
massSection = Right_pax
; More passenger seats here if needed
[MassSection.0]
name = Left_pax
stationLoadName = TT:MENU.PAYLOAD.PASSENGER_LEFT
maxMass = 300
fillProportion = 1
[MassSection.1]
name = Right_pax
stationLoadName = TT:MENU.PAYLOAD.PASSENGER_RIGHT
maxMass = 300
fillProportion = 1
[MainGraph]
nodes=ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_1, ATTACH_SEAT_PAX_2, EXTERIOR_START_1, EXTERIOR_START_2, PAX_START_1
coordinate_system = relative
edges = 0, 1
massSections = Left_pax,Right_pax,Copilot
[EDGE.0]
nodeStart = EXTERIOR_START_1
nodeEnd = ENTRANCE
[EDGE.1]
nodeStart = EXTERIOR_START_2
nodeEnd = ENTRANCE
FLT Files
The FLT files required by the aircraft will depend on the aircraft being used, as explained below.
Light - Medium Aircraft (Solo / VIP Charters)
For both Solo and Vip charter missions, the pilot will start by going through the usual Preflight checks, and so these aircraft will need to have the Apron.flt setup as follows:
- Section
[SimVars.0]must have the parameterSimOnGroundset totrue. - All defined
[Covers]need to be set totrue(see here for more information). - Section
[Controls.0]must have the parameterParkingBrakeset to 100.00 (if the aircraft has a parking brake). - Aircraft electrics and engines must be turned off.
- The aircraft flight parameters (trim, flaps, etc...) should be set for a cold and idle aircraft.
An additional FLT file is required - the ApronWithoutCovers.flt file - for those occasions when the user may skip the preflight phase and there is an RTC event, or when something causes a Back On Track event after preflight. This file should be set up like a regular apron FLT file, however you should ensure that these changes are made:
Airliners (VIP Charter)
For Airliner VIP Charter missions, you do not need an Apron.flt, and should instead be using the ApronWithBatteriesWithoutCovers.flt, setup as follows:
- Section
[SimVars.0]must have the parameterSimOnGroundset totrue. - All defined
[Covers]need to be set tofalse(see here for more information). - Section
[Controls.0]must have the parameterParkingBrakeset to 100.00 (if the aircraft has a parking brake). - Engines must be turned off.
- The communication system (and thus, the electrics system) must be turned on.
- The aircraft flight parameters (trim, flaps, etc...) should be set for an idle aircraft.